Legal and Environmental Consequences of AFFF Exposure
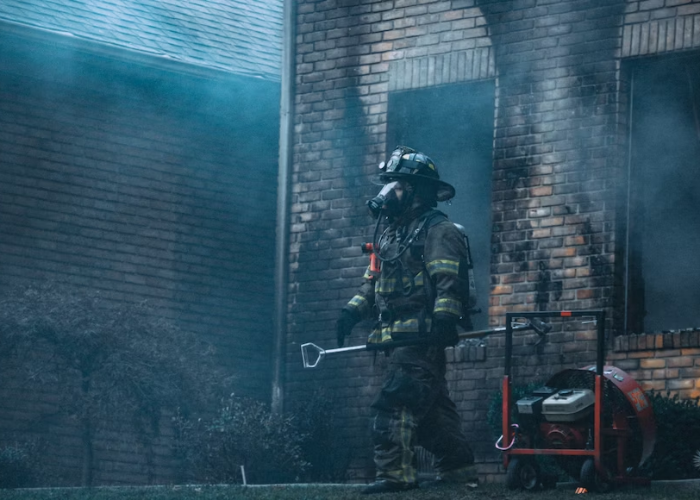
Aqueous Film Forming Foam (AFFF), a fire suppressant used to combat flammable liquid fires, has played a crucial role in firefighting for decades. However, its environmental impact and associated health risks have come under scrutiny due to the presence of toxic per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
According to the New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services, PFAS have been used for decades in Class B firefighting foam. The use of this type of foam presents an urgent public health challenge. Urgent action is needed to limit future contamination and reduce exposure to firefighters and civilians.
In this article, we will dive into the environmental implications of AFFF contamination and the resulting legal consequences.
The Role of AFFF and PFAS
AFFF’s effectiveness in controlling fires involving flammable liquids like petroleum is undeniable. It works by creating a foam blanket that cools the fire and forms a film, depriving the fire of oxygen.
However, the inclusion of PFAS compounds, such as PFOS and PFOA, has raised concerns. PFAS, known as “forever chemicals,” don’t break down easily and can accumulate in the environment, leading to long-term contamination. This persistence underscores the need to reevaluate AFFF’s overall impact.
Health and Environmental Risks
PFAS contamination from AFFF has infiltrated soil, groundwater, and drinking water sources near military bases, firefighting training facilities, and industrial sites. Studies have linked PFAS exposure to various health issues, including cancer, immune system disruption, and developmental problems.
Moreover, bioaccumulation of PFAS in wildlife and aquatic ecosystems further exacerbates environmental concerns. According to the National Library of Medicine, these substances have been observed to accumulate within the protein-rich tissues of fish. Most of them cannot be removed by simple cooking. These risks highlight the urgent need to address and mitigate AFFF-related contamination.
Legal Actions and Accountability
The legal landscape surrounding AFFF has evolved as evidence of its detrimental effects surfaced. Numerous affected people have filed a firefighter foam lawsuit. Lawsuits against manufacturers like 3M and DuPont have multiplied, alleging that they knew about the health risks associated with PFAS in firefighting foams.
AFFF’s inclusion in firefighting equipment testing standards, as set by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), has also come under scrutiny. This has brought the organization under potential liability. These legal battles underscore the complexity of allocating responsibility for the consequences of AFFF contamination.
Ongoing Litigation and Settlements
According to TorHoerman Law, AFFF lawsuits have gained momentum, with thousands of cases pending across the United States. As noted in a Reuters article from June, 3M has proposed a $10 billion settlement offer to address some of these claims. However, plaintiffs still have the choice to reject this offer and proceed with individual lawsuits.
The complexity of these legal battles is further demonstrated by bankruptcies among manufacturers facing mounting liabilities. These developments highlight the far-reaching implications of AFFF contamination and the challenges of achieving resolution.
Impacts on Communities and Ecosystems
AFFF contamination has far-reaching consequences. Communities around affected sites, especially those with military bases, have experienced compromised drinking water quality. Ecosystems are affected as well, with aquatic life and soil health threatened by PFAS persistence.
Contaminated water supply companies are also seeking compensation for the costs of filtering PFAS from drinking water. These impacts underscore the urgent need for comprehensive remediation efforts and the importance of prioritizing public health and environmental restoration.
Moving Toward Solutions
Addressing the AFFF contamination crisis requires multidimensional solutions. Stricter regulations, updated testing standards, and safer firefighting alternatives are vital. As noted by The Verge, 3M intends to cease the utilization of PFAS and terminate their production by the end of 2025. This phased reduction of PFAS production initiated by some manufacturers demonstrates a step toward responsibility.
Environmental cleanup efforts and ongoing research are essential to mitigate the impacts of AFFF contamination on ecosystems and public health. Collaborative efforts among industries, regulatory bodies, and environmental organizations are crucial in finding effective, sustainable solutions.
Final Word
In confronting the challenge of AFFF contamination, it’s clear that the convergence of firefighting efficacy, environmental responsibility, and public health has come into focus. The inclusion of persistent PFAS compounds in firefighting foam has triggered a cascade of legal actions, highlighting the intricate web of accountability.
As lawsuits proliferate and settlements emerge, the long-term consequences for affected communities and ecosystems underscore the critical need for comprehensive solutions. Stricter regulations, industry cooperation, and the pursuit of safer alternatives signal a shift toward responsible action.
The journey ahead requires collaboration, innovation, and a collective commitment to safeguarding both our environment and the well-being of future generations.